Chinese hacking group APT41 caught using Google tool for data theft

Google’s Threat Analysis Group Uncovers APT41’s Misuse of the GC2 Tool in Cyberattacks
Chinese state-sponsored hacking group APT41, also known as HOODOO, has been caught using Google’s open-source GC2 (Google Command and Control) red teaming tool in data theft attacks against a Taiwanese media company and an Italian job search website. Mandiant, which has been tracking APT41 since 2014, has linked the group to other known Chinese hacking groups such as BARIUM and Winnti.
Google’s Threat Horizons Report in April 2023 revealed that the threat actors used the GC2 tool to deploy additional payloads on compromised devices and exfiltrate stolen data to Google Drive. The report also highlights a trend of threat actors shifting to legitimate red teaming tools and remote monitoring and management (RMM) platforms to evade detection.
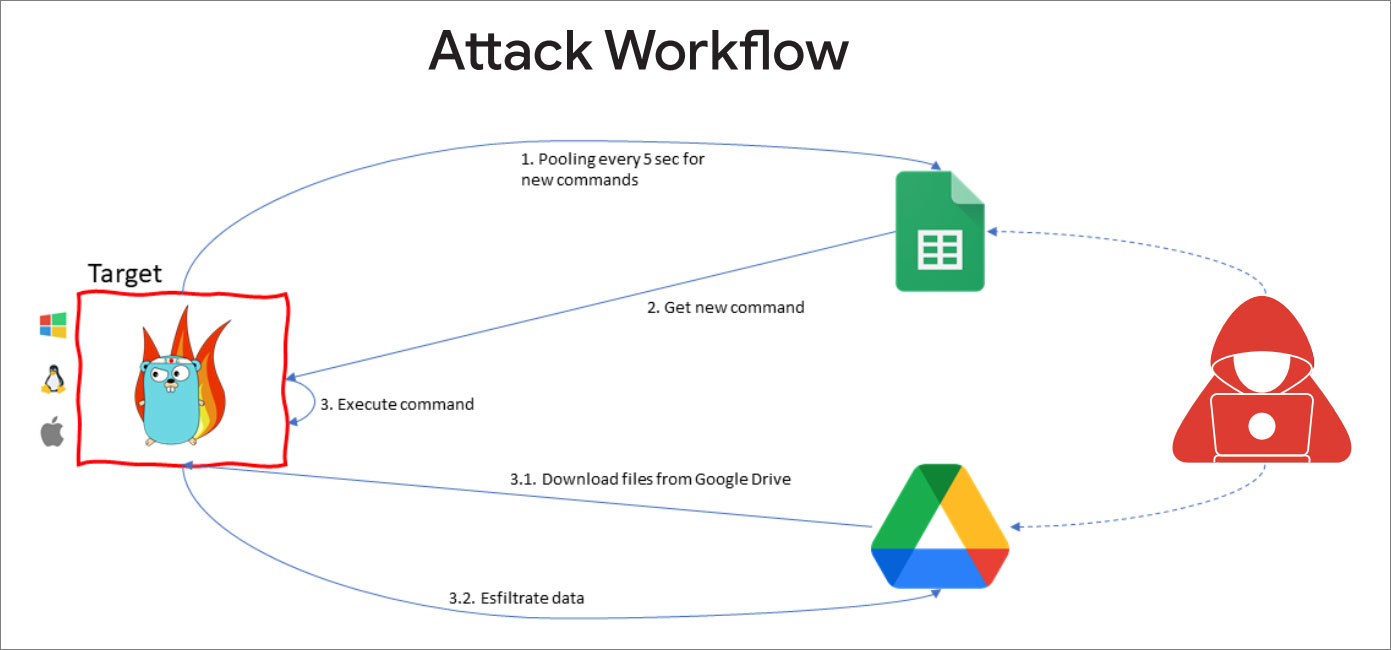 APT41 GC2 attack workflow
APT41 GC2 attack workflow
Source: Google
APT41’s Use of Legitimate Tools Highlights Trend of Threat Actors Evading Detection
APT41’s use of GC2 further highlights the trend of threat actors moving to legitimate red teaming tools and RMM platforms to evade detection during their attacks. While the use of Cobalt Strike has been widespread for years, it has also led to significant investments into detecting it in attacks, making it more easily spotted by defenders. As a result, threat actors have started to shift to other red teaming tools, such as Brute Ratel and Sliver, to evade detection during their attacks.
Ransomware gangs have also begun abusing the Action1 RMM tool for persistence on compromised networks and to execute commands, scripts, and binaries. Unfortunately, any tool that can help red teamers conduct exercises or for admins to manage a network remotely can equally be abused by threat actors in their own attacks.
Offensive Security, Bug Bounty Courses
APT41’s use of GC2 in phishing attacks against media and job search companies
Google’s report notes that TAG disrupted an APT41 phishing attack against a Taiwanese media company that attempted to distribute the GC2 agent through phishing emails. APT41 also used GC2 in attacks against an Italian job search website in July 2022. While it is not known what malware was distributed in these attacks, APT41 is known to deploy a wide variety of malware on compromised systems, including rootkits, bootkits, custom malware, backdoors, Point of Sale malware, and even ransomware in an isolated incident.
In 2020, the Department of Justice indicted three Chinese nationals believed to be part of APT41 for conducting supply chain attacks, data theft, and breaches against countries worldwide.
In conclusion, APT41’s use of GC2 is just one example of how threat actors are constantly evolving their tactics to evade detection. As defenders invest more in detecting widely used tools such as Cobalt Strike, threat actors will continue to shift to new tools that are less likely to be detected. As such, it is imperative that defenders stay vigilant and adapt their strategies to detect and prevent these attacks.
Are u a security researcher? Or a company that writes articles or write ups about Cyber Security, Offensive Security (related to information security in general) that match with our specific audience and is worth sharing?
If you want to express your idea in an article contact us here for a quote: [email protected]
Source: bleepingcomputer.com









