PikaBot Malware Strikes: Malvertising Campaign Targets AnyDesk Users
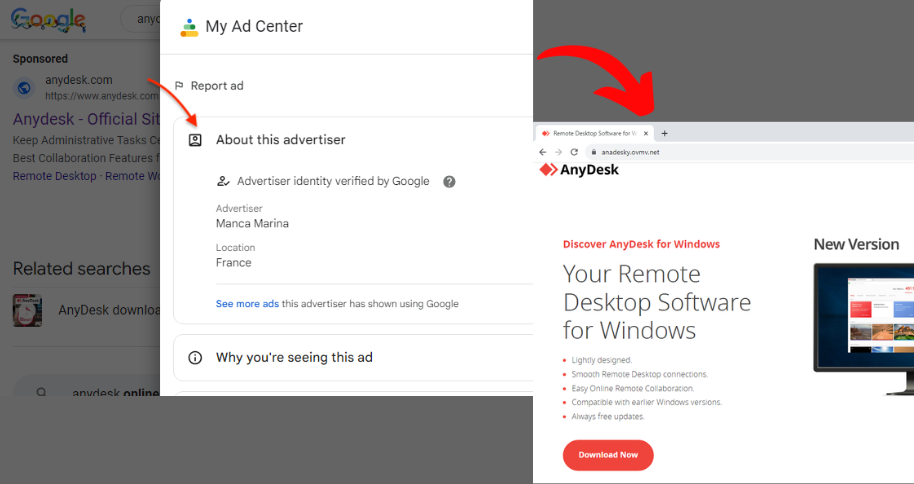
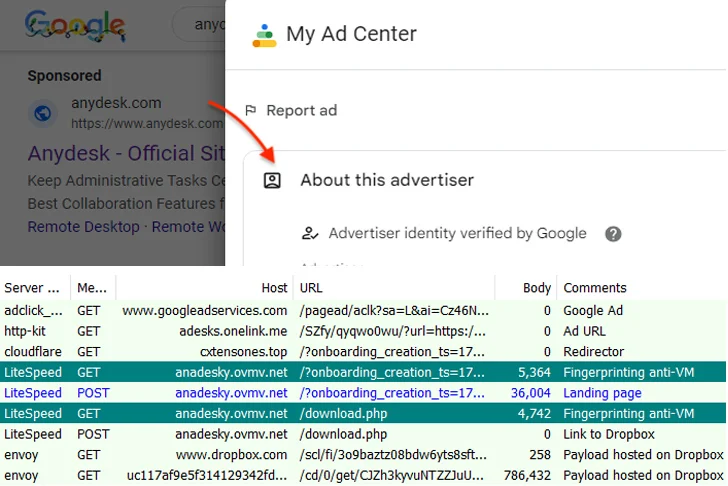
A new malware loader known as PikaBot has been identified as part of a malvertising campaign that specifically targets users searching for legitimate software such as AnyDesk. According to Jérôme Segura of Malwarebytes, PikaBot, previously distributed via malspam campaigns, has now emerged as a preferred payload for the threat actor TA577.
See Also: So, you want to be a hacker?
Offensive Security, Bug Bounty Courses
Malwarebytes has highlighted that these attacks bear resemblance to previously identified malvertising chains used to disseminate another loader malware known as FakeBat (aka EugenLoader). This suggests a common process used by different threat actors, possibly indicating a form of ‘malvertising-as-a-service’ where Google ads and decoy pages are provided to malware distributors.
Trending: Recon Tool: PassDetective
Are u a security researcher? Or a company that writes articles or write ups about Cyber Security, Offensive Security (related to information security in general) that match with our specific audience and is worth sharing?
If you want to express your idea in an article contact us here for a quote: [email protected]
Source: thehackernews.com










